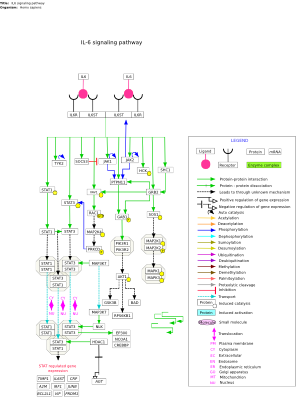
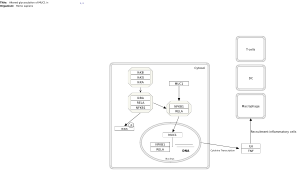
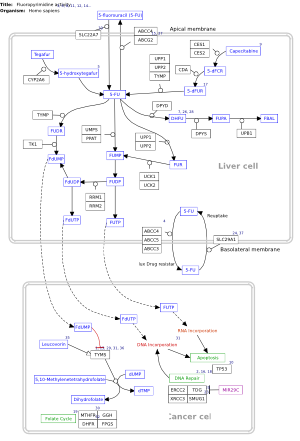
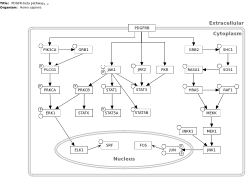
Portal:CPTAC
From WikiPathways
CPTAC Pathways
Welcome to the CPTAC Pathway PortalThis portal highlights pathway content relevant to the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC). The National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, announced the launch of a Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium in August 2011. CPTAC is a comprehensive and coordinated effort to accelerate the understanding of the molecular basis of cancer through the application of robust, quantitative, proteomic technologies and workflows. The overarching goal of CPTAC is to improve our ability to diagnose, treat and prevent cancer. To achieve this goal in a scientifically rigorous manner, the NCI launched CPTAC to systematically identify proteins that derive from alterations in cancer genomes and related biological processes, and provide this data with accompanying assays and protocols to the public. The pathways included in this portal have been organized into classic cancer hallmark categories, based on the different biological capabilities acquired during the multistep development of human tumors. To read more, see Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation, Hanahan and Weinberg, Cell 2011. | 
|
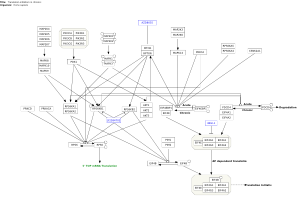
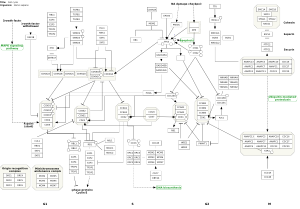
Cancer Hallmark Categories
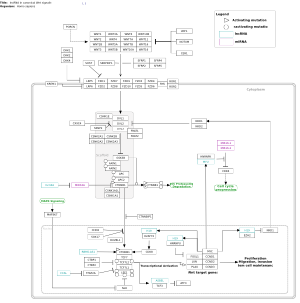
Featured Pathways
|
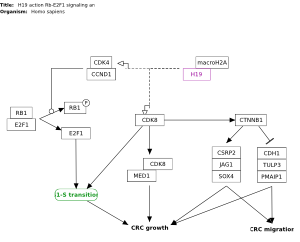
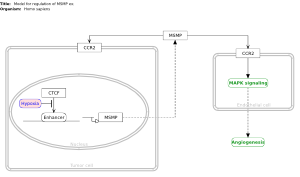
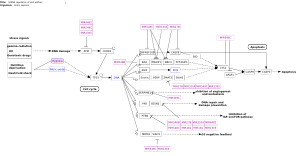
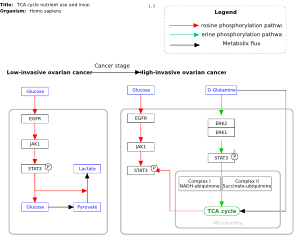
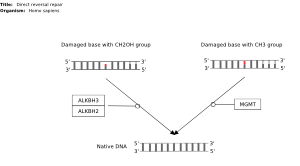
Zhang, et al. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of Human High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer |
| View featured pathways |
| List of all pathways for this portal |
Assay Portal
CPTAC also includes an Assay Portal to widely disseminate highly characterized proteomic assays to the global research community, with access to SOPs, reagents, and assay characterization/validation data
Resources
- Over 2400 protein and peptide assays: Browse assays
- Over 750 antibodies and antigen targets: Browse antibodies
- Hundreds of terabytes of data sets: Browse data
Learn how they incorpated WikiPathways images with custom links on their site.
Pathway Curation
On this page you see rotating displays of hallmark and featured pathways. Where did these pathways come from? They came from people like you! The CPTAC set of pathways can be edited, fixed and added to using the pathway drawing and annotation tools here at WikiPathways.
Getting Started
- Introduction to WikiPathways (slides)
- WikiPathways Overview or New Contributor Quickstart
- General help pages
- CPTAC Workshop Exercises
Resources
- Learn more about CPTAC
- Pathway analysis
- Cytoscape and the WikiPathways app
- PathVisio and the WikiPathways plugin
Curation projects
- Curating Hallmark Pathways -- How to
- Example: construction of Pathways in Renal Cancer
- Contact Alex Pico if interested in curating, adding or using CPTAC pathways, [email protected]