Help:Guidelines EditorPalette
From WikiPathways
(→Line types) |
(→MIM Interactions - Molecular Interaction Maps) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Stimulation | !Stimulation | ||
| - | !Catalysis | + | ![[Pathway:WP550|Catalysis]] |
| - | !Transcription-Translation | + | ![[Pathway:WP554|Transcription-Translation]] |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:MIM-Stimulation2.png]] | |[[Image:MIM-Stimulation2.png]] | ||
| - | |[[Image:MIM-Catalysis.png | + | |[[Image:MIM-Catalysis.png]] |
| - | |[[Image:Transcription.png | + | |[[Image:Transcription.png]] |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 01:32, 5 July 2014
This guide describes the recommended uses of the most commonly used elements of the WikiPathways editor palette. Examples are taken directly from the WikiPathways archives. If you have questions about specific cases, contact the discussion mailing list.
Contents |
Basic Interactions
Line / Arrow
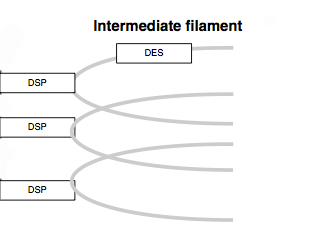
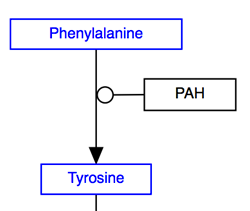
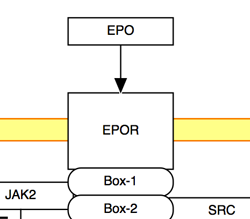
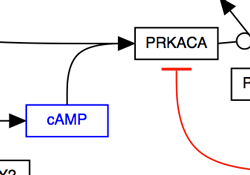
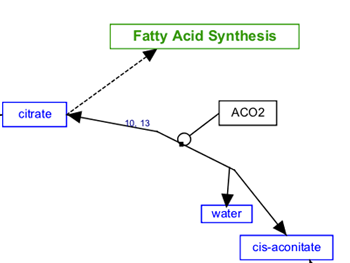
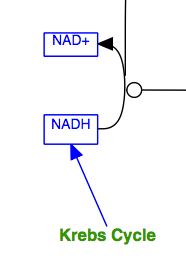
The solid line and arrow are used to denote a variety of processes, including conversion, translocation, activation, binding and modification.
| Conversion | Receptor binding | Translocation between compartments | Activation by cAMP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 
| 
| 
|
Dashed line / dashed arrow
The dashed line and arrow are used to denote an uncertain process or a process that involves additional steps not outlined in the current diagram.
| Multi-step process without details |
|---|

|
T-bar
The T-bar is used to denote inhibition.
| Inhibition by transcriptional regulation |
|---|
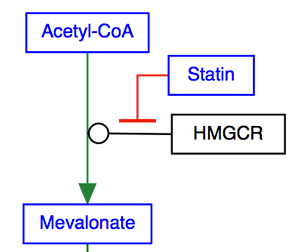
|
Line types
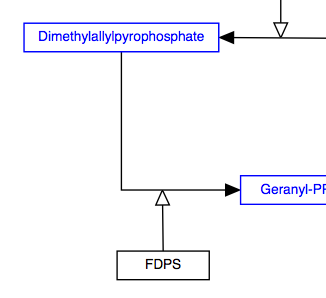
Any interaction can have a line style of either straight, curved, elbow or segmented. The default style is straight, and is shown in the examples above. The other three line styles are used primarily to increase readability of complex pathways.
| Curved | Elbow | Segmented |
|---|---|---|
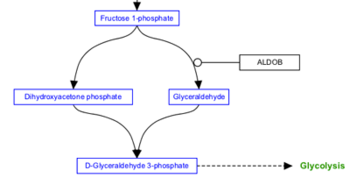
| 
| 
|
MIM Interactions - Molecular Interaction Maps
The WikiPathways editor includes a set of MIM interaction types, based on the Molecular Interaction Maps notation. Refer to the MIM specification for details on recommended usage.
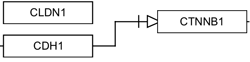
| Necessary stimulation | Binding | Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| 
| 
|
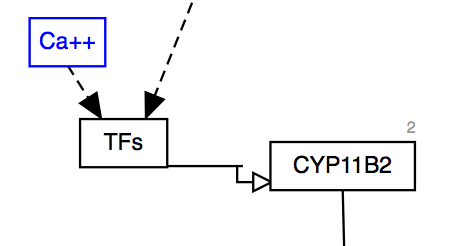
| Stimulation | Catalysis | Transcription-Translation |
|---|---|---|
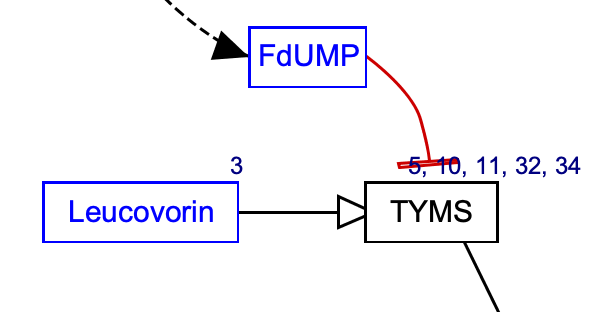
| 
| 
|
Data nodes
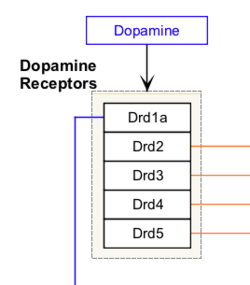
- GeneProduct: Default data node and used for genes, RNA and/or proteins.
- RNA: Used specifically for RNA, for example miRNA.
- Protein: Used specifically for proteins.
- Metabolite: Used for any metabolite, drug or small molecule.
- Pathway: Used instead of a label to denote a connection to another pathway.
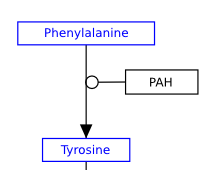
| GeneProduct, Metabolite, Pathway | RNA | Protein |
|---|---|---|

| 
| 
|
Graphical elements
Graphical elements are purely graphical, meaning they do not have a meaning in the network graph that defines nodes and interactions.
Label
Labels are used to describe locations, entities, processes or context:
| Labels used to indicate cell type and event | Labels used to describe complexes |
|---|---|

| 
|
Line
Lines can be used to denote cellular structures such as membranes.
Arc
The arc is typically used to denote a cellular or molecular structure.
Rectangle
The rectangle is typically used to enclose a set of entities or annotations:
Cellular compartments
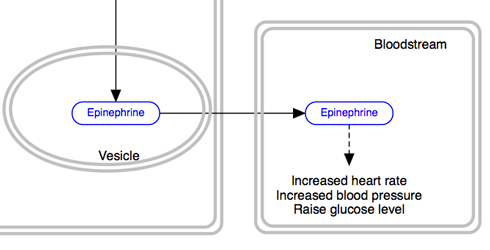
Cellular compartment shapes are used to specify the cellular location of processes. Using the defined cellular compartment shapes also ensures that this information is encoded in the gpml.
| Cell | Nucleus | Vesicle |
|---|---|---|
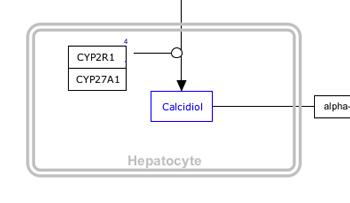
| 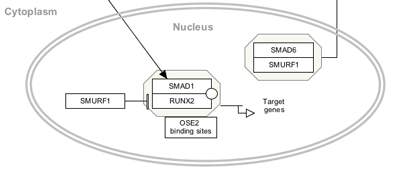
| 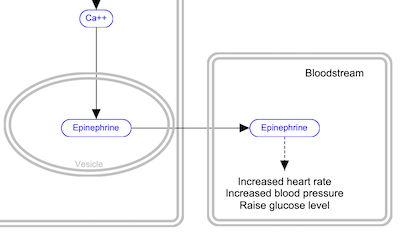
|